For the the overshooting day (it was yeserday) we offer you this article from Rwanda
Introduction:
Ecology is defined as the scientific study of the distribution and abundance of organisms, the interaction between organisms and their environment.
The environment is the totality of nature and natural resources, but also includes the cultural heritage and the infrastructure constructed by humans to facilitate socio-economic activities. The natural resources include land/soil, water, forests and vegetation cover, livestock, fish and other wildlife; the minerals under the land and the air which envelopes the earth’s surface; and human beings.
Rwanda is endowed by resources in the environment largely determine the nature and amount of exploitation and utilization of resources. Perception has changed through various stages of human history and with advancement of knowledge about the earth and its resources. The thinking of most people and cultures largely influences the way they treat their environment.
Why do Rwandans overexploit the resources?
Continued human population growth has led to unsustainable rates of consumption of our natural resources, resulting in a loss of Earth’s biodiversity. The main factors driving biodiversity loss include habitat destruction, climate change, invasive species, overexploitation, and pollution.
• High Population
• Unemployment (white-colour job)
• Ignorance on reuse
• Laxity in law enforcement (applicazione)
• Poor agricultural practice e.g. large herds of cattle (mandrie bestiame)
• Cultural factors e.g., keeping of large livestock
• Economic factors e.g., wealth – people tend to exploit to get wealth
Roles of youth with Rwandan government on the conservation of environment
A. The forest resources
A forest is a part of ecosystem in which vegetation plays a major role in biogeochemical cycles.
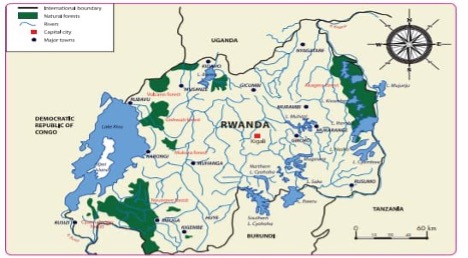
Rwanda has major forest that support life system of wildlife and support rainfall which are Nyungwe in south-west of Rwanda, Gishwati and Mukura in west part of Rwanda as well as Virunga forest in north part.
Functions of forest
✓ Forests are habitat of various organisms
✓ Global recycling of water and oxygen and carbon (chemical part) & absorbs carbon which depletes ozone layer
✓ Plants releases oxygen for animal survival
✓ Holds soil particles together (roots) reducing erosion
✓ Provide wood/ timber for construction
✓ Source of income
✓ Forest provide raw materials (industrial development) (crudo)
✓ Medicinal purposes
✓ Water catchment area (water shed conservation) (raccolta acqua)
✓ Ecotourism (tourist attraction)
✓ Source of fuel
Threats faced forest in Rwanda and impacts
Rwandans are carrying different activities that lead to elimination of trees cover the place such as deforestation, road construction, construction of their houses and cattle keeping.
Removal of trees from a place can cause swift erosion, a shift in a surviving land species, a different pattern of terrestrial wild life and changes in the life of a stream through silt deposition. They can lead to climate change.
Forest management strategies
• Rwandans are encouraged to increase the place covered by forest through ‘ITORERO RY’IGIHUGU PROGRAM’ aimed to teach youth from secondary schools Rwandan values include preservation of forest.
• Sustained yield- this means that the number of trees harvested should not exceed the number replaced by new growth. It also emphasis harvesting in a manner that will minimize soil erosion and therefore enhances the ability of the forest to regenerate
• Fire suppression or use of controlled burns
• Selective harvesting or clear cutting
• Encouraging zero grazing
B. Water management
In Rwanda water supply plays crucial role for the economic and social purpose. The government have been established measures to deal with water issues.
Threats faced by water in Rwanda:
• Industrial and domestic waste
• There is a growing demand for water as population increase. Consequently, there has been much exploitation of underground water.
• Modernization in agriculture, use of fertilizer affect aquatic animal’s life.
Opportunities to reduce wastage of water
• Improve irrigation and domestic distribution system to reduce linkage and evaporative processes.
• ‘Supply on demand” strategy e.g., by use of metering and realistic pricing
• Reduce demand for instance, the use of smaller toilet cisterns, more efficient irrigation, etc.
• Repairing linkage water pipes.
• Cautious water transfer from surplus areas to shortage areas.
• Cautious storage in dams, reservoirs and tanks to keep rain water.
C. Soil resource
Soil is a natural body of animal, mineral and organic constituents differentiated into horizon of variable depth which differ from material below in morphology, physical make up, chemical properties of composition and biological characteristics.
How soil loss fertility?
✓ Leaching and Erosion (wind erosion water erosion)
✓ Human activities e.g. mono-cropping, deforestation, overgrazing, burning of land, poor farming
✓ Poor drainage poor
✓ High population
✓ Natural occurrence or hazard e.g. flooding
Conservation of soil resource.
Youth people are encouraged to have great attention on natural resources through especially schooling with their participation in
• Participation of youth from rural places in making terraces
• Zero-grazing business adopted by cattle keepers
• Modern methods of practicing agriculture among young people who involve in agro-business
• Youth are getting different ways of controlling population growth which increase overuse of land and land conflict.
D. Wild life resources
Examples of protected areas in Rwanda
Volcanoes National Park is a national park in northwestern Rwanda. It covers 160 km² of rainforest and encompasses five of the eight volcanoes in the Virunga Mountains, namely Karisimbi, Bisoke, Muhabura, Gahinga and Sabyinyo. Mountains are favorable for different kind of animals such as mountain gorillas in Rwanda volcanic chains.
Nyungwe National Park lies in southwest Rwanda, partly abutting the Burundi border. It’s a vast area of mountain rainforest, home to many species of chimpanzees, plus owl-faced and colobus monkeys. The Canopy Walkway, part of the Igishigishigi Trail, is a high suspension bridge with views over the valley and surrounding forests. A trail runs to the Kamiranzovu Marsh, with its birdlife, orchids and waterfall.
Akagera National Park lies in eastern Rwanda, hugging the border with Tanzania. It’s characterized by woodland, swamps, low mountains and savannah. The varied terrain shelters wildlife including zebras, giraffes, elephants, lions and hundreds of bird species, such as the rare shoebill stork. In the southern part of the park, vast Lake Ihema is home to hippos and crocodiles.
Gishwati Forest is a forest in the north-western part of Rwanda, not far from Lake Kivu. It is a forest surrounded by suitable pasture that support dairy farming and well-being people. Gishwati also is near to IBERE RYA BIGOGWE region where young cattle keepers develop their business as well preserving domestic animals.
Mukura National Park is a protected reserve in the northwest part of Rwanda, covering about 1,200 km.
Threats that harm forest as well as game reserve and wildlife preserved there are deforestation, bad weather condition and wildfire.
E. Wetlands: natural and irrigated
Wetlands are part of the green infrastructure of healthy catchments. They protect water quality, maintain water supplies, and reduce flooding risks necessary to sustain socio-economic development. Wetlands provide a critical habitat for wildlife and play pivotal roles in ecosystems.
Most of Rwandan youth involves in the activities aimed to preserve wetland and use them for leisure purpose. The biggest wetlands are floodplain wetlands of low altitude associated with major lakes such as Lake Cyohoha, Rweru, Mugesera, Nasho, and rivers, such as Nyabarongo, Akanyaru, Mukungwa, Base, Nyabugogo, among others.
Rwanda has shown commendable political will and taken tangible actions to address wetlands degradation and unsustainable use of water resources. To ensure sustainable utilization of wetlands.
Role of youth to the conservation of wetland:
• Participating in the community work (UMUGANDA PROGRAM)
• In the short term, all illegal activities in wetland must be avoided through the involvement of youth in environment protection measures.
• Over the long term, we need to work together so that other unsustainable activities operating within wetlands come to an end.
Here there are Responsibilities of REMA (Rwanda Environment Management Authority)
- To implement government environmental policy
- To advice the government on policies, strategies and legislations to the management of the environment as well as the implementation of environment related international conventions, whenever deemed necessary
- To conduct thorough inspection of environment management in order to prepare report on the status of environment in Rwanda that shall be published in every 2 years
- To put in place measures designed to prevent climate change and cope with its impact
- To conduct study, research and investigations and other relevant activities in the field of environment and publish the finding.
To conclude, the environment determines the life on the earth, when environment is cared make life easier and stable but also when is destroyed leads to harmful (dannoso) effects to people, we need to work together as youth with all stakeholders to maintain ecology as most important factor that support life on the earth.
The story of environment of Rwanda was written by Olivier NIYOMUBYEYI who is Rwandan. This story related to the environment of Rwanda and influence of youth in conservation and protection of environment as well as the government support.